A free flap is a technique in plastic and reconstructive surgery where any type of tissue is lifted and completely detached from its original location (donor site) and transplanted to another distant location (recipient site). This is distinct from a pedicled flap, in that the transplanted tissue is completely detached from its blood supply at the original location and requires reconnection of an artery and vein at the recipient site to re-establish circulation.
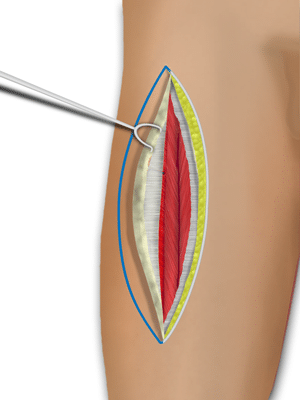
Anterolateral Thigh (ALT) Flap
In the right patient, the skin and subcutaneous fat of the anterolateral thigh can be quite thin, making this flap a potentially large donor site of supple and sometimes sensate fasciocutaneous tissue.
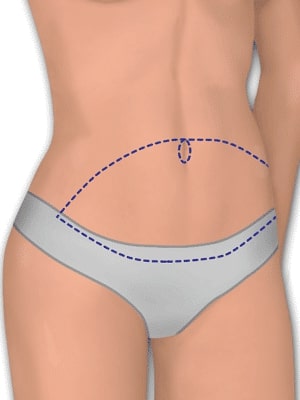
Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator (DIEP) Flap
The DIEP flap can be used for a variety of reconstructive procedures when a large segment of soft tissue, including fat and skin is necessary. It has become more popular for breast reconstruction, but requires significant microsurgical experience to harvest.
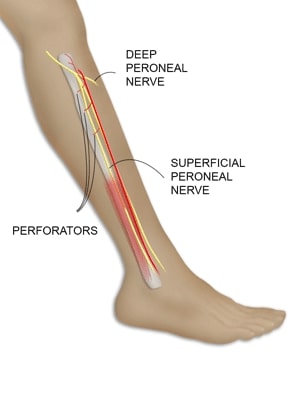
Fibula Flap
The reliability of the skin paddle harvested with the fibula flap has been questioned. Strategies to increase reliability have included harvesting a greater length of paddle and septum and trying to predict the location of septal perforators.
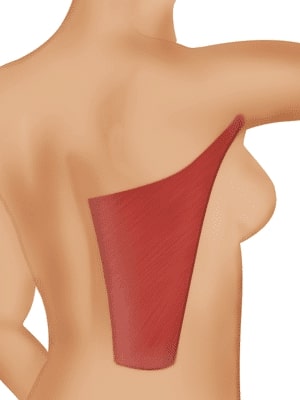
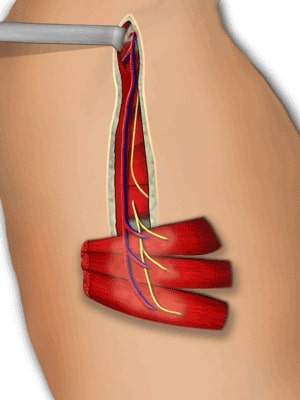
Latissimus Dorsi Flap
The latissimus dorsi muscle is the largest muscle in the body, up to 20 by 40 centimeters, allowing coverage of extremely large wounds. In spite of its size, no significant donor functional deficit results from removal of the muscle.
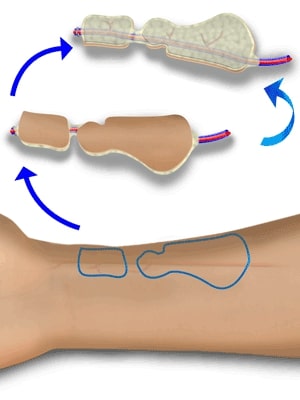
Radial Forearm Flap
The skin of the volar forearm provides relatively thin and reliable coverage for a wide variety of defects. Because the radial aspect of the arm is hair bearing, the amount and quality of the hair is a consideration in using this flap for resurfacing.
Serratus Flap
The serratus anterior muscle takes origin from the lateral scapula and fans anteriorly as it inserts into the first nine ribs. Only a portion of the muscle is used for flap reconstruction: the lower three slips of muscle arise at the very inferior scapula and have an independent blood and nerve supply, making them a good source of a medium to small sized muscle for free flap coverage.
All images and links used with permission from Dr. Rudy Buntic.